Dell OpenManage™ IT Assistant User's Guide
| NOTE: In IT Assistant, the term "system" is used to refer to a computer system (notebook, desktop, or server), network switch, remote access controller (RAC), or server module (server in a modular system) that is attached to a network. |
| NOTE: You must enable discovery for systems to be discovered. See "Setting Discovery Options." |
IT Assistant discovers instrumented and noninstrumented systems on subnets, at IP address ranges on a subnet, and at Internet Protocol (IP)/Internetwork Packet eXchange (IPX)/host name addresses. To discover all the systems on a subnet, a range of systems on a subnet, or an individual system at a specific IP/IPX/host name address, you must add (register) that subnet, subnet IP address range, or IP/IPX/host name address.
| NOTE: A subnet, range of IP addresses on a subnet, single host name, single IP address, or single IPX address are known collectively in IT Assistant as "discovery ranges." |
Discovery begins as soon as you register a discovery range.
NOTE: Server Agent 4.x supports discovery through IPX, but
does NOT support systems management through IPX. For IT Assistant to manage IPX-only
systems, you must load one of the following on the managed node:
If you are managing systems running Novell® NetWare® using IPX only, Dell recommends that you use the internal network address of the managed node followed by a node address of 000000000001. |
The address specification entry field adjusts based on the discovery range type you selected; these adjustments help you to enter the correct address specification format. The following are examples of valid address specifications for each discovery range type:
- Subnet — 193.109.112.*
- Host name — mynode.dell.com
- Node IP address range — 193.109.112.45-99
- Node IP address — 193.109.112.99
- IPX address — 00006112.00aa00bbccdd
Systems discovered on the newly registered discovery ranges begin to display in the system tree.
NOTE: The following are
important points to know about discovery:
|
| NOTE: In IT Assistant, the term "system" is used to refer to a computer system (notebook, desktop, or server), network switch, remote access controller (RAC), or server module (server in a modular system) that is attached to a network. |
| NOTE: The IT Assistant services store requests for system removal in a queue. If you remove a system and then reboot it before the IT Assistant services process the removal request, you must remove the system again. |
You can remove a single system, a range of IP addresses on a subnet, or an entire subnet from the discovery process. Removed systems, IP address ranges, and subnets are no longer discovered until re-added (reregistered). You can remove systems in two ways: by removing the discovery range configuration settings or by using the Remove Discovered System command. Removing systems through the discovery range configuration settings permanently removes the system from the system tree. The Remove Discovered System command removes the system only until the next discovery cycle.
To remove a single system, a range of IP addresses on a subnet, or an entire subnet by modifying the discovery range configuration settings, perform the following steps:
IT Assistant removes the system or systems from the discovery range configuration and also from the system tree display.
NOTE: IT Assistant does not inform you when a discovery cycle is in
progress. If you remove a discovery range during a discovery cycle, and IT Assistant is discovering
that discovery range when you remove it, the following three things happen:
This results in some systems (the ones that were not yet discovered when you removed the discovery range remaining in the system tree. You must remove these systems again using the following procedure. |
To remove a single system by using the Remove Discovered System command, perform the following steps:
To make a system easier to find, you can sort the list by clicking Status, Host Name, System Type, Power State, or IP Address.
IT Assistant removes the selected system from the system tree display. However, if the system is still listed in the discovery range settings, the system is rediscovered and redisplayed during the next discovery cycle.
| NOTE: In IT Assistant, the term "system" is used to refer to a computer system (notebook, desktop, or server), network switch, remote access controller (RAC), or server module (server in a modular system) that is attached to a network. |
IT Assistant discovers active, instrumented and noninstrumented systems on the registered discovery ranges and displays them in the systems window. The systems are listed in an expandable system tree and are categorized by system type. The first level of the system tree consists of the categories All Systems, Custom Groups, Desktops, Network Switches, Portables, Servers, Unclassified, and Workstations.
| NOTE: If IT Assistant is able to classify all discovered systems, the category Unclassified does not appear. |
The IT Assistant network monitoring service performs system discovery and classification. If the IT Assistant network monitoring service can classify a system, it places that system within the Desktops, Network Switches, Portables, Servers, or Workstations category branches of the system tree. If the IT Assistant network monitoring service cannot classify a system, it places the system within the Unclassified category branch. You can create custom groups from systems within any of these categories.
| NOTE: If you move a system into a custom group, it remains listed within its original classification group and in the All Systems group. |
| NOTE: RACs are network entities that have IP addresses, so IT Assistant discovers them. However, RACs are not instrumented, so IT Assistant displays them as Unclassified entities in the system tree. |
The icon next to the system name is the system status indicator. See "Status Indicators" for descriptions of these icons.
| NOTE: IT Assistant discovers systems on registered discovery ranges only. You must register discovery ranges before systems display in the systems window. |
When an alert condition exists for a system, IT Assistant retrieves a system status from the instrumentation on the system that generated the alert. IT Assistant may then update the system status indicator in the system tree. The alert appears in the alerts window, and its severity is indicated by an alert indicator to the left of the alert entry. The alerts window and the Logs tab in the systems window also provide additional information about the event.
Status indicators also display beside systems for which no specific alerts have been received. These are the healthy and unknown indicators described in "Status Indicators."
Modular systems, such as the Dell PowerEdge™ 1655MC, comprise several systems, as "systems" are defined in IT Assistant terminology. One chassis usually comprises an Embedded Remote Access/MC (ERA/MC) controller, a managed network switch, and one or more server modules. Each of these chassis elements are systems capable of being discovered by IT Assistant.
In the system tree, IT Assistant represents a modular system and its component systems in two ways:
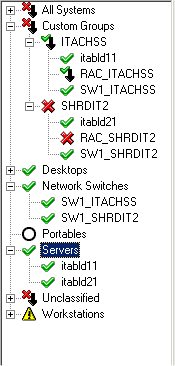
| NOTE: These are simple examples only; modular systems generally have many more than one server module installed. |
IT Assistant creates the custom group for a modular system by default. If you want to rename the custom group to something more readable than a Service Tag, select Options® Custom Groups® Edit.
| NOTE: IT Assistant does not automatically remove a modular system's custom group, even if you remove all of the group's components. You must manually remove custom groups created for modular systems. |
Modular system support and its integration with Server Administrator (which complements IT Assistant by providing additional server-specific functions and capabilities) make IT Assistant an ideal management tool for modular systems. Because Server Administrator is installed on each server module, you can use IT Assistant to launch Server Administrator against the server module you want to manage. When finished, you can manage other server modules in the same chassis by clicking another module in the IT Assistant system tree and launching Server Administrator again.
| NOTE: Using the procedures in this section, you can configure IT Assistant to support DMI, SNMP, and CIM discovery and communication. However, you can disable protocols using the configservices utility. If you disable any of these protocols after a discovery range has been discovered, IT Assistant requires a subsequent discovery cycle to unregister that protocol so that it is not used for discovery or communication. |
To set preferences for the default discovery process, perform the following steps:
To edit options for discovery range, perform the following steps:
IT Assistant enables you to force a discovery cycle on all or selected systems. You may want to do this to confirm a system's status or to refresh old status data before the next scheduled discovery interval.
To force a restart of the discovery process, perform the following steps:
If you see a misclassified system or know an unclassified system is actually of a specific type, you can reclassify it.
| NOTE: The IT Assistant network monitoring service classifies systems based on DMI 2.0 or Dell-specific instrumentation. If your network comprises a variety of vendor systems, many will likely be unclassified. |
To reclassify a discovered system, perform the following steps:
| NOTE: This action reclassifies the system in the
IT Assistant data repository, which is installed on the management station; the reclassification persists until you change it again using this procedure. If you want the IT Assistant network monitoring service to attempt to classify manually reclassified systems, reclassify those systems as Unclassified, and the service will attempt to classify them during the next discovery cycle. |
To view summary information about a discovered system, perform the following steps:
| NOTE: The amount of information displayed on the Summary
tab depends on the amount of information available from a managed system's
instrumentation. If the system's instrumentation does not report information
for a particular field, or if the instrumentation that IT Assistant
queries for a particular field is not present, that field is left blank. For example, for servers instrumented with Server Agent 4.2 or earlier, IT Assistant sometimes retrieves the information for the Network Data section of the Summary tab from the Intel® NIC instrumentation agent. If this agent is not present, the Network Data section is left blank. In this particular case, you can resolve the issue by loading the Intel NIC instrumentation or upgrading to a later version of Server Agent or Server Administrator. |
| NOTE: Only Dell-instrumented systems support this feature. |
To view status information about a discovered Dell system, perform the following steps:
The left pane of the Status tab contains the status tree, which shows the status of the currently selected system's components. The right pane of the Status tab contains status information about the component currently selected in the status tree. Main System Chassis is the default selection, and the right pane displays the General Status of the chassis. Clicking any other root- (first-) level component also displays the General Status for that component.
| NOTE: All systems have the root-level component Main System Chassis. Other root components, such as ERA or Disk Storage, appear only if the system is configured with that component. |
Clicking any leaf- (second-) level component displays the Individual Element Status of that component. If you click another system in the system tree, the Status tab displays the corresponding information for the new system (if that system is equipped with the same type of component). Using IT Assistant in this way enables you to quickly check the status of a specific component for different systems.
| NOTE: When you view Embedded Devices in the status tree, some devices might appear twice, although only one device exists. |
| NOTE: If IT Assistant takes a very long time to display the IT Assistant Status tab for a server that is running Server Administrator, you can reduce this time by suppressing the status display. See "Status Display Suppression Script" for more information. |
| NOTE: Only Dell-instrumented systems support this feature. |
IT Assistant enables you to view user names for Dell clients and servers. Client systems support a single password; this is the one configured in their system BIOS. Servers can have multiple users, each with their respective passwords.
To view user information about a discovered system, perform the following steps:
The Users tab lists the currently defined users for the selected system.
See "User Setup for Systems and Remote Access Hardware."
See "CIM, DMI, and SNMP Information."
To search for systems among the registered IP/IPX/host name addresses, perform the following steps:
The available selections in the Find controls change dynamically based on the filters and qualifiers you specify. The third criterion control may prompt you for a text string rather than a menu selection, depending on your settings in the first and second controls.
Systems that match the search criterion or criteria you specify display in the lower pane of the SEARCH window. You can sort the list according to a system property by clicking the column header button for that property, such as Host Name or IP Address.
System name resolution is the networking term for the process of matching IP addresses to host names. To configure system name resolution, click Discovery Cycle on the IT Assistant navigation tree and use the Discovery Cycle Configuration dialog box. If you select DNS Name Resolution, the name of the system is resolved through DNS first; if you select Instrumentation Name Resolution, the system name is resolved through instrumentation first (if the managed node is instrumented), then through DNS if instrumentation fails. If you upgrade an older version of IT Assistant to this version, you may notice that some system names have changed.
If (1) you set up event filters to use specific system names as filter criteria, and (2) you have selected instrumentation name resolution, IT Assistant attempts to resolve the system's IP address using all events received through its discovered system database. If the system was not discovered, then IT assistant attempts resolution through DNS to provide the correct system name that the filter requires.
| NOTE: If a system's instrumentation name is different from its name as resolved by DNS, and DNS goes down during a discovery cycle, the system can appear in the system tree with a different name, resulting in two entries for the same system. |
| NOTE: If you rename a system but keep its IP address the same, the system could have duplicate entries in the system tree. Because of the common use of Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) in network environments, IT Assistant does not attempt to resolve such duplications. You must manually delete any duplicate system tree entries. |