Back to Contents Page
Jumpers and Switches—A General Explanation
• Disabling a Forgotten Password • I/O Board Labels • I/O Riser Board LabelsJumpers and switches provide a convenient and reversible way of reconfiguring the circuitry on a printed circuit board. When reconfiguring the system, you may need to change jumper settings on the system board. You may also need to change jumper and/or switch settings on expansion cards or drives.
| CAUTION:Make sure the system is turned off before you change a jumper setting. Otherwise, damage to the system or unpredictable results may occur. |
Switches control various circuits or functions in the computer system. The switches you are most likely to encounter are dual in-line package (DIP) switches, which are normally packaged in groups of two or more switches in a plastic case. Two common types of DIP switches are slide switches and rocker switches (see the following illustration).
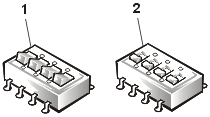
1 |
Rocker switch |
2 |
Slide switch |
Each of these switches has two positions, or settings. To change the setting of a slide switch, use a small, pointed object such as a small screwdriver or a straightened paper clip to slide the switch to the proper position. To change the setting of a rocker switch, use the screwdriver or paper clip to press down on the appropriate side of the switch. In either case, do not use a pen, pencil, or other object that might leave a residue on the switch.
Figure 1 shows the location and defaults of the switches on the system input/output (I/O) board. See Table 1 for the designations, defaults, and functions of the system's switches.
Figure 1.System Board Switches
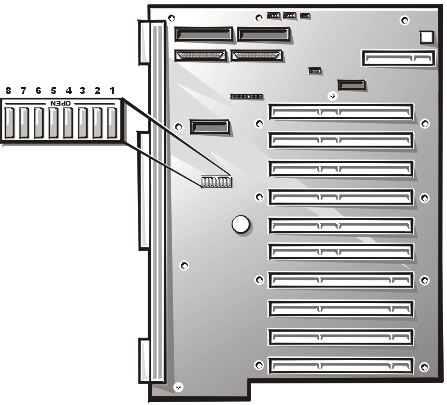
| Table 1.System-Board Switch Settings |
| Switch Position | Function | Settings | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reserved | Open | Reserved (do not change). |
| 2 | BIOS Recovery | Open Closed |
The normal BIOS boot sector
is used at system boot (default). The recovery boot sector is used at system boot. |
| 3 | Reserved | Open | Reserved (do not change). |
| 4 | Reserved | Closed | Reserved (do not change). |
| 5 | CMOS Clear | Open Closed |
The configuration settings
are retained at system boot (default). The configuration settings are cleared at next system boot. (If the configuration settings become corrupted to the point where the system won't boot, change the switch setting and boot the system. Reset the switch to "Closed" before restoring the configuration information.) |
| 6 | Password Clear | Open Closed |
The password feature is
enabled (default). The password is cleared at next system boot. |
| 7 | PCI hot plug switch | Open Closed |
Enable PCI hot plug switches.
Disable PCI hot plug switches (default). |
| 8 | Reserved | Open | Reserved (do not change). |
| NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the Abbreviations and Acronyms list. | |||
Jumpers are small blocks on a circuit board with two or more pins emerging from them. Plastic plugs containing a wire fit down over the pins. The wire connects the pins and creates a circuit. To change a jumper setting, pull the plug off its pin(s) and carefully fit it down onto the pin(s) indicated.
A jumper is referred to as open or unjumpered when the plug is pushed down over only one pin or if there is no plug at all. When the plug is pushed down over two pins, the jumper is referred to as jumpered. The jumper setting is often shown in text as two numbers, such as 1-2. The number 1 is printed on the circuit board so that you can identify each pin number based on the location of pin 1.
Figure 2
shows the location of the microprocessor speed jumpers on the system profusion board. To access the microprocessor speed jumpers, remove the fan bay assembly (see steps 1 through 8 in Upgrading or Adding Cache Coherency Filters). Table 2 lists the functions of these jumpers.Figure 2. Microprocessor Speed Jumpers
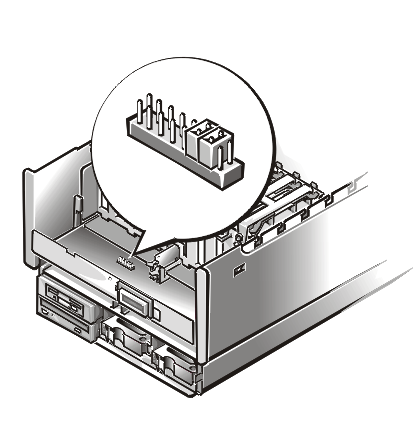
Table 2. Microprocessor Speed Jumper Settings
| Jumper Settings | Description |
|---|---|
|
The microprocessor's internal speed is 500 MHz. |
|
The microprocessor's internal speed is 550 MHz (when available). |
|
The microprocessor's internal speed is 600 MHz (when available). |
|
The microprocessor's internal speed is 650 MHz (when available). |
|
The microprocessor's internal speed is 700 MHz (when available). |
|
The microprocessor's internal speed is 750 MHz (when available). |
| NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the Abbreviations and Acronyms list. | |
The computer's software security features include a system password and a setup password, which are discussed in detail in "Using the System Setup Program," of the User's Guide. A password switch on the I/O board enables or disables the password features and clears any password(s) currently in use.
To disable a forgotten system or setup password, perform the following steps.
| CAUTION: See Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge. |
NOTE: If you assign a new system and/or setup password with the jumper plug still installed, the system disables the new password(s) the next time it boots.
To assign a new system password using the system setup program, see "Assigning a System Password" in the User's Guide. To assign a new setup password using the system setup program, see "Assigning a Setup Password" in the User's Guide.
Table 3 lists the connectors and sockets located on the input/output (I/O) board.
| Table 3. I/O Board Connectors and Sockets |
| Connector or Socket | Description |
|---|---|
| BATTERY | Battery connector |
| FLOPPY | Diskette-drive interface connector |
| PCIn | PCI expansion-card connectors |
| SCSI A, SCSI B | Internal (SCSI A) and external (SCSI B) Ultra2/LVD SCSI connectors |
| NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the Abbreviations and Acronyms list. | |
Table 4 lists the connectors and sockets located on the I/O riser board.
| Table 4. I/O Riser Board Connectors and Sockets |
| Connector or Socket | Description |
|---|---|
| MONITOR | Video connector |
| KEYBD | Keyboard connector |
| MOUSE | Mouse connector |
| PARALLEL | Parallel port connector; sometimes referred to as LPT1 |
| SERIALn | Serial port connectors; sometimes referred to as COM1 and COM2 |
| REMOTE | Server Management serial port |
| NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the Abbreviations and Acronyms list. | |