![]() Forwarding
Tagged/Untagged Frames
Forwarding
Tagged/Untagged Frames
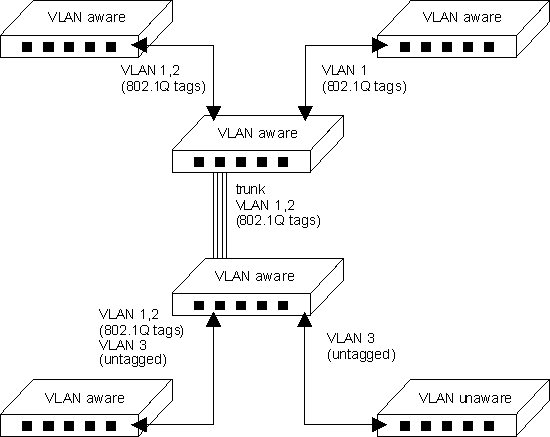
VLAN operation on the switch is enabled by default. Therefore, all frames are transferred internally through the switch with a VLAN tag. This tag may already be on the frame entering the switch, or added to the frame by the switch. VLAN information already existing on frames entering the switch is automatically handled by the switch. The switch learns VLAN information from tagged frames and appropriately switches frames out the proper ports based on this information. The configuration of VLANs for frames entering the switch without tags must be manually configured. This configuration can be made either through the web or console interface, or via SNMP.
Before enabling VLANs for the switch, you must first assign each port to the VLAN groups it will participate in. By default, all ports are assigned to VLAN 1 as untagged ports. You should add a port as a tagged port (that is, a port attached to a VLAN-aware device) if you want it to carry traffic for one or more VLANs and the device at the other end of the link also supports VLANs. Then assign the port at the other end of the link to the same VLANs. However, if you want a port on this switch to participate in one or more VLANs, but the device at the other end of the link does not support VLANs, then you must add this port as an untagged port (that is, a port attached to a VLAN-unaware device).
Port-based VLANs are tied to specific ports. The switch’s forwarding decision is based on the destination MAC address and its associated port. Therefore, to make valid forwarding and flooding decisions, the switch learns the relationship of the MAC address to its related port—and thus to the VLAN—at run-time.
Packets received by the switch are treated in the following ways:
| NOTE: You can change port VLAN membership settings in the VLAN Membership page. |
Port overlapping can be used to allow access to commonly shared network resources among different VLAN groups, such as file servers or printers. Note that if you implement VLANs which do not overlap, but still need to communicate, you must connect them using a router or Layer 3 switch.
Ports can be assigned to multiple tagged or untagged VLANs. Each port on the switch is therefore capable of passing tagged or untagged frames. To forward a frame from a VLAN-aware device to a VLAN-unaware device, the switch first decides where to forward the frame, and then strips off the VLAN tag. However, to forward a frame from a VLAN-unaware device to a VLAN-aware device, the switch first decides where to forward the frame, and then inserts a VLAN tag reflecting this port’s default VID. The default port VLAN ID is 1, but this can be changed from the VLAN, Port Settings page.