Back to Contents Page
Using Intel® PROSet in Windows*: Intel® Network Adapters User Guide
Overview
Installing Intel PROSet
Using Intel PROSet
Configuring Teams
Configuring IEEE VLANs
Uninstalling Intel PROSet
Intel PROSet is an advanced configuration utility that lets you test Intel
network adapters and configure standard and advanced features. This file
describes the installation and usage of Intel PROSet on servers running Windows* Server 2003 and Windows 2000.
Back to Top
 |
NOTE: You must have administrative rights
on the computer where you are installing the software. |
When you run the installer, it checks to see if a previous version of the drivers or Intel PROSet exists on your computer. If a previous version exists, it is upgraded to the latest version. Any settings specified in the previous version are applied to the upgrade version.
 |
NOTE: If you downloaded the Intel PROSet
installation files from Dell's Web site, run proset.msi from the
\Mgmt_Apps\APPS\PROSet\W2KWS03\ directory. |
- From the Autorun screen, click Install Software. If the Autorun screen
does not appear, double-click autorun.exe from the root of the media.
The installation dialog box
appears.
- Click Next to continue with the installation. If the installer has not run before, a dialog box appears with the license agreement.
- Click
I accept the terms in the license agreement to accept the agreement,
then click Next.
- In the Setup Type dialog, click:
- Typical to install adapter drivers and Intel PROSet
- Custom to select the features you would like to install
- Click Next.
- If you selected Typical, click Install.
If you selected Custom, the Custom Setup dialog appears and lists the features you can install.
- To select or deselect a feature for installation, click the icon adjacent to the feature. If the feature has one or more sub-features, use the plus (+) sign to expand the tree.
For information about how to select or deselect features, click Help.
- To change the installation location, click Change and then browse to the new location.
- To ensure there is enough disk space on the local drive for the selected features, click Space.
After customizing the installation, click Next. Then click Install.
- Click Finish.
The Installer closes.
After installing Intel PROSet and restarting the computer, two icons appear, as shown below. Double-click either icon to run Intel
PROSet.
| System Tray Icon: |
 |
| Control Panel Icon: |
 |
You can also start Intel PROSet by selecting it in the Start -> Programs menu.
Back to Top
The main Intel PROSet window is similar to the illustration below. To set advanced parameters, select the desired adapter in the left window and click the
Advanced tab. You may also right-click your mouse to add the selected adapter to a team or VLAN. Be sure to click
Apply or OK on the main
Intel PROSet window to apply any changes you have made. See the Intel PROSet online help for additional information.
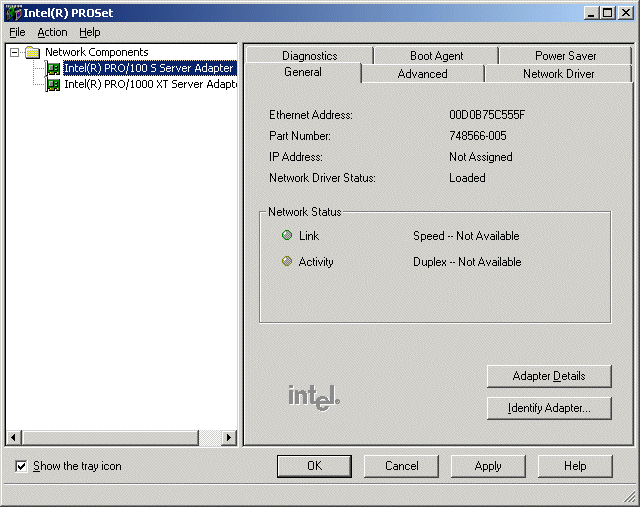
Intel PROSet runs when you double-click the Intel PROSet tray icon or the Intel PROSet
icon in the
Control Panel.
Back to Top
In Windows, teams are set up using Intel PROSet. For instructions and
information, refer to the Intel PROSet Help. To access Help, open Intel PROSet and click the Help menu at the top of the screen.
 |
NOTE: Intel Teaming is compatible with Microsoft Network Load Balancing (NLB/WLBS) running on Windows
2000 and Windows Server 2003 when in multicast mode only. |
Creating a team
- In Intel PROSet, right-click an adapter you want to include in a team.
- Click Add to Team, then click Create New Team.
The Teaming Wizard appears.
- Select the type of team you want to create, then click Next.
For more information on team types, see Set
Up Adapter Teaming.
- Select the adapters you want to include in the team by clicking the
appropriate checkboxes, then click Next. Clear an adapter's checkbox if
you do not want to include that adapter in the team.
- Click Finish to create the team.
- Click OK or Apply.
 |
NOTE: If you wish to set VLANs on a team,
you must first set up the team. |
Adding an Adapter to an Existing Team
- In the Network Component Tree in Intel PROSet, right click on a team
listing.
- In the menu that appears, click Add Adapter to Team, and then
select the adapter you want to add.
- Be sure to match offloading and other feature settings for all adapters in
the team.
Renaming a Team
- Right-click the team name, then click Rename Team.
- In the Rename Team dialog box, type the new team name, then click OK.
Removing a Team
- In the Network Component Tree in Intel PROSet, right click on a Team
Listing.
- In the menu that appears, click Remove Team.
A confirmation message appears.
- Click OK.
 |
NOTE: If you defined a VLAN or QoS
Prioritization on an adapter joining a team, you may have to redefine it
when it is returned to a standalone mode. |
Back to Top
In Windows, you must use Intel PROSet to set up and configure VLANs. For instructions, see the Intel PROSet Help. To access Help, open Intel PROSet and click the Help menu.
The following versions of Microsoft Windows support Intel PRO adapters when configured for VLANs:
- Windows 2000
- Windows Server 2003
A maximum of 64 VLANs can be used on a server.
You cannot re-enable a VLAN once it has been disabled. To re-enable the connection, disable all adapters, then restart the server.
 |
CAUTION: VLANs cannot be used on teams that contain non-Intel network adapters. |
 |
CAUTION: Use Intel PROSet to add or remove a VLAN. Do not use the Network and Dial-up Connections dialog box to enable or disable
VLANs. Otherwise, the VLAN driver may not be correctly enabled or disabled. |
 |
NOTE: If you will be using both teaming and
VLANs, be sure to set up teaming first. |
Setting Up a VLAN
- Create a VLAN on the switch. Use the parameters you assign there to join
the VLAN from the server. See your switch documentation for more information.
- Start Intel PROSet.
- If your server has multiple adapters, right-click the desired adapter or
team in
Intel PROSet.
Note that VLANs can be assigned to a team, but teams should be set up before
VLANs.
- From the menu that appears, click Add VLAN.
You may see a dialog asking you to enable 802.1Q tagging. This is required for
VLANs. Click Yes to enable the tagging if you see this dialog.
- Enter the VLAN ID and VLAN Name.
The VLAN ID must match the VLAN ID on the switch. Valid ID range is from
1-4094, though your switch might not support this many IDs. The VLAN Name is
for information only and does not have to match the name on the switch. The VLAN Name is limited to 256 characters.
- Click OK.
Repeat steps 3-5 for each VLAN you want the server to join.
The VLANs you add are listed in the Virtual LANs box and in the Windows Device
Manager.
- Click Apply or OK.
Removing a VLAN
- In Intel PROSet, right-click on the VLAN you want to remove.
- From the menu that appears, click Remove VLAN.
If you are removing the last VLAN from the system, you will see a dialog box
informing you that packet tagging will be disabled.
- Click OK.
- Click Apply or OK to apply your changes.
Back to Top
Uninstalling Intel PROSet
You do not need to uninstall Intel PROSet unless you are permanently removing all Intel adapters. You
can uninstall Intel PROSet using either Add
or Remove Programs or the
installation CD.
 |
NOTE: Before uninstalling Intel PROSet, you must remove teams and VLANs configured in Intel PROSet. |
Uninstalling Intel PROSet with the Installation CD
- Insert the installation CD in the CD-ROM drive. If the Autorun screen
does not appear, double-click autorun.exe from the root of the media.
The CD autorun program starts.
- Click Install Software.
The InstallShield Wizard screen appears.
- Click Next.
- Click Remove, then click Next.
- Click Remove.
- Click Finish to exit the wizard.
The installer removes Intel PROSet from the computer.
Uninstalling with Add or Remove Programs
- From the Control Panel, double-click Add or Remove Programs.
(Windows 2000 users, double-click Add/Remove Programs.)
The Add or Remove Programs window appears.
- Select Intel(R) PROSet, then click Remove.
- When the confirmation message appears, click Yes.
Please read all restrictions
and disclaimers.
Back to Contents Page
Back to Top
