 Front-Bezel Indicators
Front-Bezel IndicatorsDell™ PowerEdge™ 6650 Systems User's Guide
 Front-Panel Indicators and Features
Front-Panel Indicators and Features
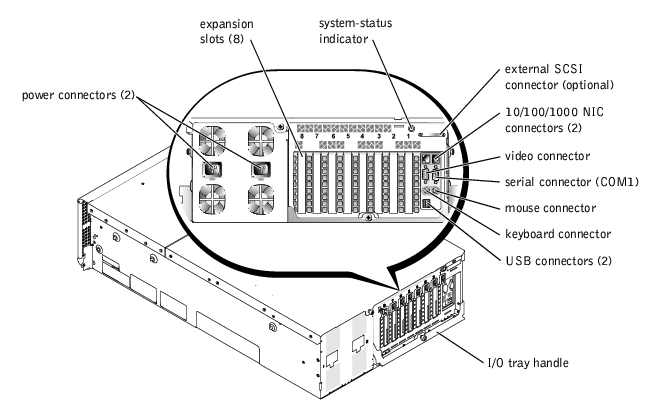
 Back-Panel Indicators and Features
Back-Panel Indicators and Features
 Obtaining Technical Assistance
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Your system is a high-performance enterprise server offering new levels of performance and scalability with up to four Intel® Xeon™ microprocessors and 16 GB of system memory, as well as hot-pluggable redundant hard drives, expansion slots, power supplies, and system fans.
This section describes the major hardware and software features of your system and provides information about the indicators on the system's front and back panels. It also provides information about other documents you may need when setting up your system and how to obtain technical assistance.
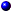
The system's bezel has an indictor that can represent system status when the bezel is installed (see Figure 1-1). The indicator signifies when the system is operating properly or when the system needs attention. The back-panel system-status indicator functions the same as the bezel indicator. A caution code signifies a problem with power supply, system or power-supply fans, system temperature, hard drives, or expansion cards.
Table 1-1 lists the system's status indicator codes and the system's back-panel status indicator codes.
Figure 1-1. System Status Indicators
|
Bezel Indicators |
Back-Panel Indicator |
Indicator Code | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Status |
Caution | ||
Off | Off | Off | No power is available to the system, or the system is not powered on.1 |
On | Off | Blue | The system is operating normally. |
Off | Blinking | Amber blinking | The system has detected an error and requires attention. |
Blinking | Off | Blue blinking | The system is identifying itself. NOTE: Systems management software causes the status indicator to blink to identify a particular system. For more information, see the systems management software documentation. |
1 See your Installation and Troubleshooting Guide for more information. | |||
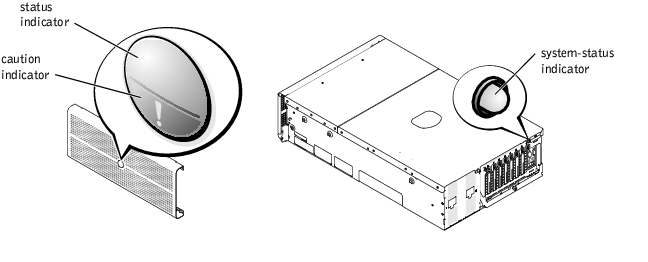
Additional indicators are located behind the bezel for system power and hard drives. The CD and diskette drives have green activity indicators. The front-panel LCD display provides status information using an alphanumeric character display (see "LCD Status Messages"). See Figure 1-2 for the front-panel indicators and features.
Figure 1-2. Front-Panel Features and Indicators
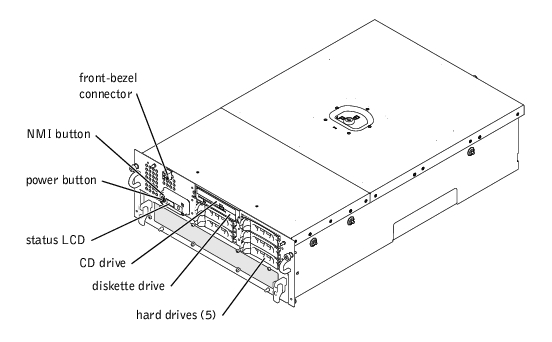
The power button is used to turn the power supplies on and off, while the NMI button is used for debugging (see your Installation and Troubleshooting Guide for more information).
 |
NOTE: If you turn off the system using the power button and the system is running an ACPI-compliant operating system (such as Microsoft® Windows® 2000), the system performs a graceful shutdown before the power is turned off. If the system is not running an ACPI-compliant operating system, the power is turned off immediately after the power button is pressed. |
The system's front-bezel indicator shows whether the system is operating correctly or whether it needs attention (see Figure 1-1). When the status and/or caution indicator indicates an error condition, open the bezel for more information provided on the LCD.
The LCD displays two lines of five alphanumeric characters. The display codes are presented in two color combinations:
For more information about LCD status messages, see your Installation and Troubleshooting Guide.
Each hard-drive carrier has two indicators that provide information on the status of the SCSI hard drive: a busy indicator and a status indicator (see Figure 1-3 and Table 1-2).
Figure 1-3. SCSI Hard-Drive Indicators
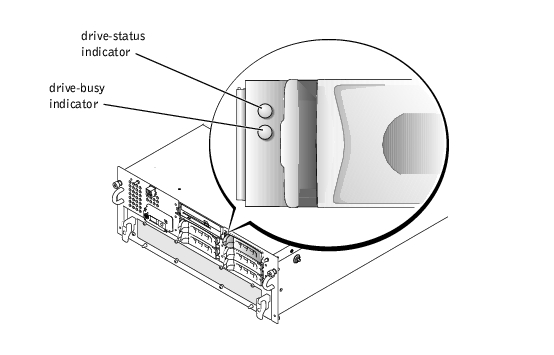
The drive-busy indicator lights when data is transferred to or from the hard drive. The drive-status indicator denotes whether the hard drive is active on the SCSI bus. This indicator is controlled by the hard drive.
Table 1-2 lists the drive status indicator codes controlled by the backplane board firmware. Different codes are displayed as drive events occur in the system. For example, in the event of a hard-drive failure, the "drive failed" code appears. After the drive is selected for removal, the "drive being prepared for removal" code appears, followed by the "drive ready for insertion or removal" code. After the replacement drive is installed, the "drive being prepared for operation" code appears, followed by the "drive online" code.
|
Indicator |
Indicator Code |
|---|---|
Drive bay empty, ready for insertion or removal | Off |
Drive being prepared for operation, drive online | Steady green |
Identify drive | Blinks green four times per second |
Drive being prepared for removal | Blinks green twice per second at equal intervals |
Drive rebuilding | Blinks green twice per second at unequal intervals |
Drive failed | Blinks amber four times per second |
Predicted failure for the drive | Blinks green, then amber, and then off, repeating this sequence every two seconds |
NOTE: The drive-busy indicator signifies whether the hard drive is active on the SCSI bus. This indicator is controlled by the hard drive. | |
Figure 1-4 shows the back-panel indicators and features of the system.
 |
NOTE: The back-panel system status indicator has the same functionality as the status indicator. When the system is operating normally, the back-panel indicator is blue. When the system needs attention, the amber indicator blinks. |
Figure 1-4. Back-Panel Features
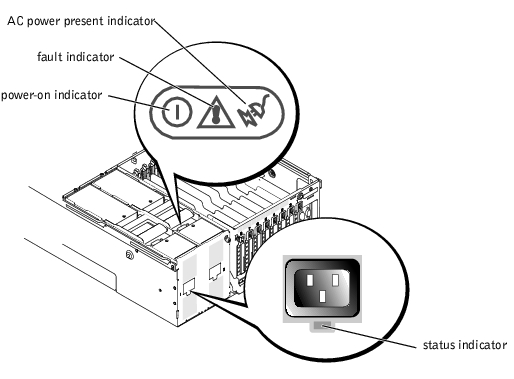
Each hot-pluggable power supply has indicators that provide information on the presence of power, and power status and faults. Figure 1-5 shows the location of the indicators. Table 1-3 lists the conditions for each indicator.
Figure 1-5. Power-Supply Indicators
|
Indicator |
Indicator Code |
|---|---|
Status | Green indicates that AC power is present at the power supply. |
Power-on | Green indicates that the power supply is operational. |
Fault | Red indicates a problem with the power supply (fan failure, voltage error, etc.). |
AC power present | Green indicates that AC power is present at the power supply and that the system is connected to an AC power source. |
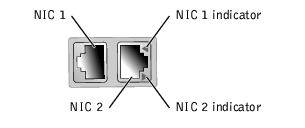
Each NIC has an indicator that provides information on network activity and link status. Figure 1-6 shows the location of the indicators. Table 1-4 lists the conditions for each indicator.
|
Indicator |
Condition |
|---|---|
Off | The NIC is not connected to the network. |
Green | The NIC is connected to a valid link partner. |
Amber blinking | Network data is being sent or received. |
An indicator is located beside each PCI hot-pluggable expansion slot (see Figure 1-7). The indicators show through the back-panel vents. Table 1-5 lists the codes for these indicators.
Figure 1-7. Expansion Slot Indicators
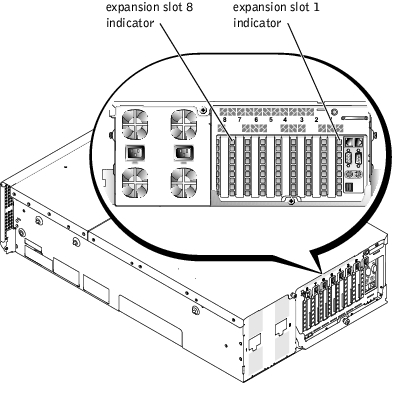
Table 1-5. Expansion Slot Indicator Codes Indicator Condition Off Expansion slot power is off. No action is required. Green Expansion slot power is on. No action is required. Green blinking fast Expansion slot is being identified by an application program or driver. No action required. Amber blinking slow Expansion card is faulty or improperly installed, causing a problem with the power supply to the card. Amber blinks twice and pauses, and then repeats the sequence Expansion card was hot-plugged that is of a slower operating speed than other cards on the same PCI bus. If you are replacing an expansion card with a card of a slower operating speed, you must power down the system to install the replacement card, or you can install the card on a bus with a compatible operating speed.
Your system offers the following features:
 |
NOTE: If you decide to upgrade your system by installing an additional microprocessor, you must order the microprocessor upgrade kits from the company where you purchased your system. Not all versions of the Intel Xeon microprocessor will work properly as additional microprocessors. The upgrade kit contains the correct version of the microprocessor as well as the instructions for performing the upgrade. All microprocessors must have the same internal operating frequency and cache size. |
 |
NOTE: Memory modules in a single memory bank must all be the same size and type. |
The system also features redundant memory, which provides your system with a failover memory bank when a memory bank fails, and a memory mirror which splits the four memory banks into a mirrored set.
 |
NOTE: Spare bank memory is supported if three or four identical memory banks (12 or 16 memory modules) are installed on your system. Memory mirror is supported if four identical banks (16 memory modules) are installed on your system. Both features must be enabled/disabled in the BIOS setup. You cannot enable both features simultaneously. For more information, see "Using the System Setup Program." |
For more information about specific features, see "Technical Specifications."
The following software is included with your system:
Your system supports the following operating systems:
A number of devices are available to protect your system from the effects of power problems such as power surges, transients, and power failures. The following subsections describe some of these devices.
Surge protectors are available in a variety of types and usually provide a level of protection commensurate with the cost of the device. Surge protectors prevent overvoltage spikes, such as those that may occur during an electrical storm, from entering the system through the electrical outlet. Surge protectors do not offer protection against brownouts, which occur when the voltage drops more than 20 percent below the normal power line voltage level.
Line conditioners go beyond the overvoltage protection of surge protectors. Line conditioners keep a system's power source voltage at a fairly constant level and provide protection from brownouts of short duration. Because of this added protection, line conditioners cost more than surge protectors—up to several hundred dollars. However, these devices cannot protect against a complete loss of power.
UPS systems offer the most complete protection against variations in power because they use battery power to keep the system running when power is unavailable or unusable. The battery is charged by the AC power while it is available so that once power is lost, the battery can provide power to the system for a limited amount of time—from 15 minutes to an hour or so—depending on the UPS system.
UPS systems range in price from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars, with the more expensive units allowing you to run larger systems for a longer period of time when power is lost. UPS systems that provide only 5 minutes of battery power let you conduct an orderly shutdown of the system but are not intended to provide continued operation. Surge protectors should be used with all UPS systems, and the UPS system should be UL safety approved.
Besides this User's Guide, the following documentation is included with your system:
You may also have the following documents.
 |
NOTE: Always read these updates before consulting any other documentation because the updates often contain information that supersedes the information in the other documents. |
If at any time you do not understand a procedure described in this guide or if your system does not perform as expected, a number of tools are provided to assist you. For more information on these help tools, see "Getting Help" in your Installation and Troubleshooting Guide.