 CIM_LogicalElement
CIM_LogicalElementDell OpenManage™ Server Administrator CIM Reference Guide
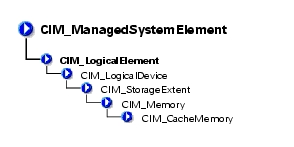
CIM_LogicalElement is a CIM-defined class containing the subclasses shown in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1. CIM_LogicalElement Class Structure

The Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF) identified in Table 3-1 lists the following characteristics for members of the CIM_LogicalElement class:
Table 3-1. CIM_LogicalElement Properties
|
Class Name: | |
|
Parent Class: |

The CIM_System class shown in Table 3-2 defines a collection of managed system elements that operates as a functional whole. An instance of the CIM_System class contains a well-defined list of components that work together to perform a specific function.
Table 3-2. CIM_System Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Indicates the name of a specific system, such as a particular storage system or server. | ||

The CIM_ComputerSystem class listed in Table 3-3 contains some or all of the following CIM_ManagedSystemElements: file system, operating system, processor and memory (volatile and/or nonvolatile storage). For properties, see Table 3-2, "CIM_System Properties."
Table 3-3. CIM_ComputerSystem Properties
|
Class Name: | |
|
Parent Class: |
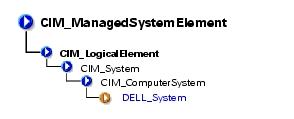
The DELL_System class listed in Table 3-4 is the set of all Dell™ instrumented systems, including server and storage systems. For properties, see Table 3-2, "CIM_System Properties."
Table 3-4. DELL_System Properties
|
Class Name: | |
|
Parent Class: |

The CIM_LogicalDevice class described in Table 3-5 models a hardware entity that may be realized in physical hardware. CIM_LogicalDevice includes any characteristics of a logical device that manages its operation or configuration. An example of a logical device is a temperature sensor's reading of actual temperature.
Table 3-5. CIM_Logical Device Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Identifies an address or other identifying information to uniquely name the logical device. | ||

The CIM_Sensor class explained in Table 3-6 contains hardware devices capable of measuring the characteristics of some physical property, for example, the temperature or voltage characteristics of a computer system.
Table 3-6. CIM_Sensor Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
The type of the sensor, for example, voltage or temperature sensor. | ||
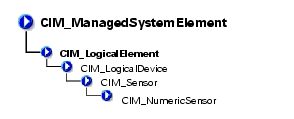
The CIM_NumericSensor class described in Table 3-7 returns numerical settings and may also support threshold settings. Figure 3-2 shows the relationship among upper and lower critical and upper and lower noncritical threshold values. The normal range falls between upper and lower noncritical thresholds.
Figure 3-2. Ranges for Threshold Values
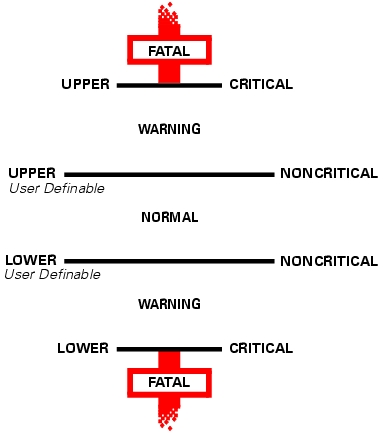
Table 3-7 provides definitions for NumericSensor properties.
Table 3-7. CIM_NumericSensor Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
An array representing the thresholds supported by this sensor. The supported values are as follows:
| ||
An array representing the thresholds that are currently enabled for this sensor. Enabled threshold values are as follows:
| ||
An array representing the writable thresholds supported by sensor. | ||
The CIM_TemperatureSensor class listed in Table 3-8 contains sensors that sample ambient temperature and return a value in degrees Celsius.
Table 3-8. CIM_TemperatureSensor Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
The CIM_CurrentSensor class listed in Table 3-9 contains sensors that measure amperage and returns a value in amperes.
Table 3-9. CIM_CurrentSensor Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |

The CIM_VoltageSensor class shown in Table 3-10 contains sensors that measure voltage and return a value in volts.
Table 3-10. CIM_VoltageSensor Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
The CIM_Tachometer class listed in Table 3-11 contains devices that measure revolutions per minute (RPM) of a fan and return the value in RPMs.
Table 3-11. CIM_Tachometer Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |

The CIM_WatchDog class described in Table 3-12 represents a timer that is implemented in system hardware. The watchdog feature allows the hardware to monitor the state of the operating system, BIOS, or a software component installed on the system. If the monitored component fails to rearm the timer before its expiration, the hardware assumes that the system is in a critical state and could reset the system. This feature can also be used as an application watchdog timer for a mission-critical application. In this case, the application would assume responsibility for rearming the timer before expiration.
Table 3-12. CIM_WatchDog Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
A string describing additional textual information about the monitored entity. | ||
Indicates the time-out interval used by the watchdog, in microseconds. | ||

The CIM_CoolingDevice class described in Table 3-13 contains a set of devices that work to keep the ambient internal temperature of the system at a safe value.
Table 3-13. CIM_CoolingDevice Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Specifies whether the device provides active (as opposed to passive) cooling. | ||
The CIM_Fan class explained in Table 3-14 contains a set of devices that work to keep the ambient internal temperature of the system at a safe value by circulating air.
Table 3-14. CIM_Fan Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |

The CIM_UserDevice class shown in Table 3-15 contains logical devices that allow a computer system's users to input, view, or hear data. Classes derived from CIM_UserDevice include CIM_Keyboard and CIM_PointingDevice.
Table 3-15. CIM_UserDevice Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Indicates whether the device is locked, preventing user input or output. | ||
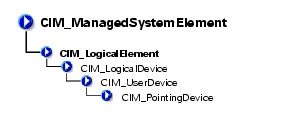
The CIM_PointingDevice class described in Table 3-16 includes those devices used to point to regions of a display. Examples are a mouse or a trackball.
Table 3-16. CIM_PointingDevice Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Indicates the type of pointing device. Values for the PointingType property are as follows: | ||
Indicates the number of buttons. If the CIM_PointingDevice has no buttons, a value of 0 is returned. | ||
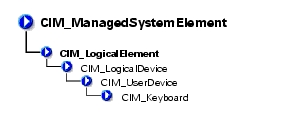
The CIM_Keyboard class explained in Table 3-17 includes devices that allow users to enter data.
Table 3-17. CIM_Keyboard Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
A free-form string indicating the format and layout of the keyboard. | ||

The CIM_PowerSupply class described in Table 3-18 contains devices that provide current and voltage for the operation of the system and its components.
Table 3-18. CIM_PowerSupply Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Indicates that the power supply is a switching power supply and not a linear power supply. | ||

The CIM_Controller class shown in Table 3-19 groups miscellaneous control-related devices. Examples of controllers are small computer system interface (SCSI) controllers, Universal Serial Bus (USB) controllers, and serial controllers.
Table 3-19. CIM_Controller Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
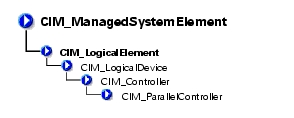
The CIM_ParallelController class identified in Table 3-20 contains a set of objects that control parallel devices. Parallel controllers transfer 8 or 16 bits of data at a time to the devices they control, for example, a parallel port controlling a printer.
Table 3-20. CIM_ParallelController Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
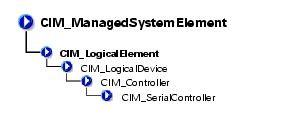
The CIM_SerialController class explained in Table 3-21 contains controllers that transfer data one bit at a time to the devices they control, for example, a serial port controlling a modem.
Table 3-21. CIM_SerialController Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Indicates the maximum baud rate in bits per second supported by the serial controller. | ||
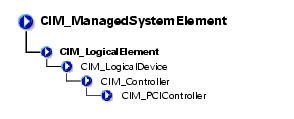
The CIM_PCIController class listed in Table 3-22 contains a set of devices that follow the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) protocol defined by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA). The PCI protocol defines how data is transferred between devices. The CIM_PCIController class contains PCI adapters and bridges.
Table 3-22. CIM_PCIController Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
|
| Values for the CommandRegister property are as follows:
| |
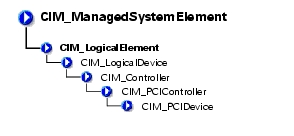
The CIM_PCIDevice class shown in Table 3-23 describes the capabilities and management of a PCI device controller on an adapter card.
Table 3-23. CIM_PCIDevice Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Identifies an array of up to six double-word base memory addresses. | ||
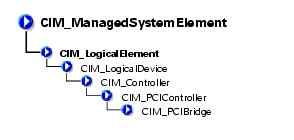
The CIM_PCIBridge class shown in Table 3-24 describes the capabilities and management of a PCI controller providing bridge-to-bridge capability. An example is a PCI to Industry-Standard Architecture (ISA) bus bridge.
Table 3-24. CIM_PCIBridge Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |

The CIM_Processor class described in Table 3-25 contains devices that interpret and execute demands, for example, the Intel® Xeon™ microprocessor.
Table 3-25. CIM_Processor Properties

CIM_StorageExtent identified in Table 3-26 contains devices that manage data storage, for example, hard drives or microprocessor memory.
Table 3-26. CIM_StorageExtent Properties
|
Class Name: | |
|
Parent Class: |
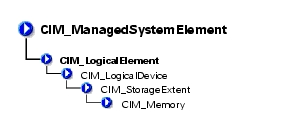
The CIM_Memory class identified in Table 3-27 describes the capabilities and management of storage extent devices, for example, cache memory or system memory.
Table 3-27. CIM_Memory Properties
|
Class Name: | |
|
Parent Class: |
The CIM_CacheMemory class explained in Table 3-28 describes the capabilities and management of cache memory. Cache memory allows a microprocessor to access data and instructions faster than normal system memory.
Table 3-28. CIM_CacheMemory Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Indicates the size, in bytes, of a single cache bucket or line. | ||

The CIM_SoftwareElement class described in Table 3-29 is used to define a CIM_SoftwareFeature. The CIM_SoftwareElement class consists of individually manageable or deployable parts for a particular platform. A software element's platform is uniquely identified by its underlying hardware architecture and operating system (for example, a system running Microsoft® Windows NT® on an Intel microprocessor). A software element's implementation on a particular platform depends on the platform's operating system.
Table 3-29. CIM_SoftwareElement Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Indicates the internal identifier for this build of the software element. | ||

The CIM_BIOSElement class listed in Table 3-30 describes the BIOS for the system. The BIOS controls the following:
Table 3-30. CIM_BIOSElement Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |

The CIM_SoftwareFeature class shown in Table 3-31 defines a particular function or capability of a product or application system. This class is intended to be meaningful to a consumer, or user of a product, rather than to explain how the product is built or packaged. When a software feature can exist on multiple platforms or operating systems (for example, a client component of a three-tiered client/server application might run on Windows NT), a software feature is a collection of all the software elements for these different platforms. The users of the model must be aware of this situation because typically they will be interested in a subcollection of the software elements required for a particular platform.
Table 3-31. CIM_SoftwareFeature Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Provides product identification such as a serial number on software. | ||

DELL_SoftwareFeature described in Table 3-32 defines the universal resource locator (URL) of the systems management software and the language in which systems management information displays. Defining these properties enables users to manage a system using an Internet browser. You can access Server Administrator using the secure hypertext transfer protocol (https) and a preassigned port number of 1311, or you can specify a port number of your own choosing.
Table 3-32. DELL_SoftwareFeature Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |

The CIM_SystemResource class listed in Table 3-33 provides access to system resources from an operating system. SystemResources consist of interrupt requests (IRQs) and direct memory access (DMA) capabilities.
Table 3-33. CIM_SystemResource Properties
|
Class Name: | |
|
Parent Class: |

The CIM_IRQ class described in Table 3-34 contains IRQ information. An IRQ is a signal that data is about to be sent to or received by a peripheral device. The signal travels by an IRQ line to the microprocessor. Each peripheral connection must be assigned an IRQ number. For example, the first serial port in your computer (COM1) is assigned to IRQ4 by default.
Table 3-34. CIM_IRQ Properties

The CIM_MemoryMappedIO class explained in Table 3-35 addresses both memory and port I/O resources for personal computer architecture memory mapped I/O.
Table 3-35. CIM_MemoryMappedIO Properties

The CIM_DMA class identified in Table 3-36 contains DMA information. A DMA channel allows certain types of data transfer between RAM and a device to bypass the microprocessor.
Table 3-36. CIM_DMA Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Identifies a part of the object's key value, the DMA channel number. | ||
Indicates the availability of the DMA. Values for the Availability property are as follows: | ||

The CIM_RedundancyGroup class shown in Table 3-37 is a set of components that provide more instances of a critical component than are required for the system's operation. The extra components are used in case of critical component failure. For example, multiple power supplies allow a working power supply to take over when another power supply has failed.
Table 3-37. CIM_RedundancyGroup Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Serves as the key for the redundancy group's instance in an enterprise environment. | ||
| ||

The CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup class explained in Table 3-38 applies to systems that have more capability and components than are required for normal operation, for example, systems that have extra fans or power supplies.
Table 3-38. CIM_ExtraCapacityGroup Properties
|
Class Name: | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Parent Class: | ||
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |

The DELL_PSRedundancyGroup identified in Table 3-39 is a Dell-specific extension of the CIM_PowerSupply class. The DELL_PSRedundancyGroup class defines what constitutes power supply redundancy in a system.
Table 3-39. DELL_PSRedundancyGroup Properties
|
Class Name: | |
|
Parent Class: |

The DELL_FanRedundancyGroup listed in Table 3-40 defines what constitutes fan redundancy in a system.
Table 3-40. DELL_FanRedundancyGroup
|
Class Name: | |
|
Parent Class: |