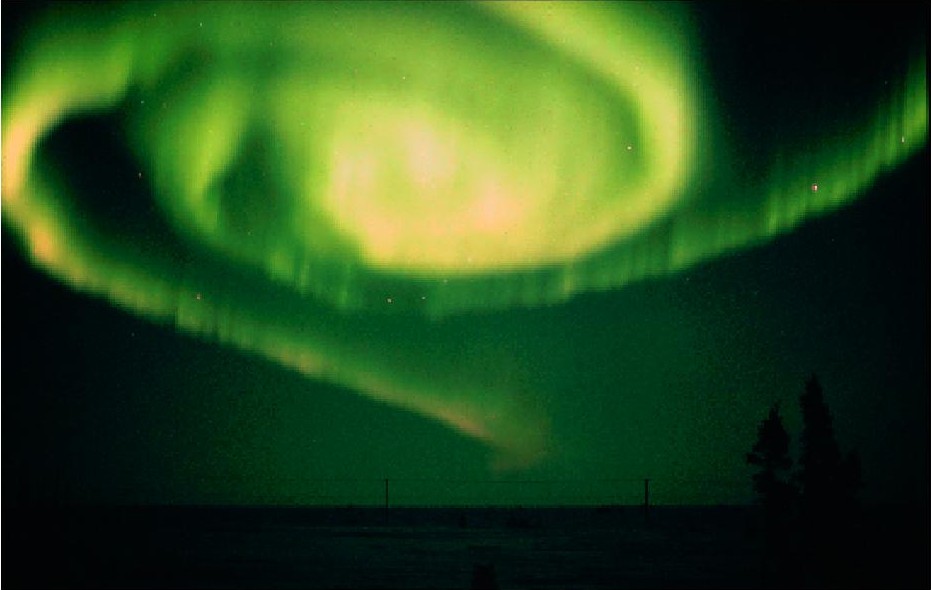


The natural phenomena, known as the Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis, are geomagnetic phenomena of impressive visual characteristics and remarkable scientific interest. Aurorae present a complex behaviour that arises from interactions between plasma (hot, ionized gases composed of ions, electrions, and neutral atoms) and Earth's electromagnetic fields. A physically-based model is devised to perform 3D visual simulations. The model takes into account the physical parameters and processes directly associated with plasma flow. The PDEs of the model are solved by a multigrid method.
 |  |
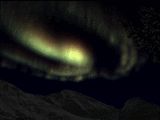
| Photograph of an auroral spiral. (Courtesy of Norbert Rosing) | Simulation of an auroral spiral showing a rayed structure and an arc break up. |
Simulation sequences (quicktime format)
 band.zip (size=14Mb)
band.zip (size=14Mb)
(Illustrate the motions and shape changes of an auroral rayed band.)
 surgeS.zip
(size=21Mb)
surgeS.zip
(size=21Mb)
(Illustrate the formation of an auroral surge in the Southern hemisphere.)
 surgeS2x.zip
(size=21Mb)
surgeS2x.zip
(size=21Mb)
(The same as surgeS, but double the speed.)
 surgeN.zip
(size=45Mb)
surgeN.zip
(size=45Mb)
(Illustrate the formation of an auroral surge in the Northern hemisphere.)