Introduction to Data Management
Database: A large and
persistent collection of (more-or-less
similar) pieces of information organized in a way that facilitates
efficient retrieval and modification.
Examples:
- inventory
- payroll
- banking and finances
- travel reservations
- computer aided design
- software development
- telecommunications data
- medical and health records
- university records
- e-commerce
- e-government
- dynamic/personalized web content
Common circumstances:
- There is lots of data (mass storage)
- Many instances of similarly structured data
- Diverse collection of application programs run against the data.
- Requirements:
- persistence and reliability
- efficient and concurrent access
- shared files or replicated data
- need to exchange data (translation programs)
- The data maintained by the system are much more important and
valuable then the system itself.
State of business in 1950s/60s
- independent applications with separate files
- growing applications base
- Problem: Every application program needed to be concerned with:
- redundancy: wasted space
- inconsistency: independent updates
- inaccuracy: concurrent updates
- incompatibility: multiple formats
- insecurity: proliferation of data to be protected
- inauditability: poor chain of responsibility
- inflexibility: changes are difficult to apply
Solution
Abstract common functions to create a uniform, well defined interface for applications accessing data
- Database Management System (DBMS): A program (or set of programs) that manages details related to
storage and access for a database.
- Model: data types supported by a database management system
- Schema: description of the interface for a specific database, including
- choice of data types for various parts of data
- specification of constraints (invariants) for the specific database
- Instance: data itself, organized to conform to the schema
DBMS provides core functionality:
- Query processing: language and algorithms for retrieving desired data
- Access control: only authorized people get to see/modify data
- Concurrency control: multiple concurrent applications access data
- Database recovery: nothing gets accidentally lost
- Database maintenance: structures are modified to accommodate evolving needs
Fundamental principle
Data independence: Applications
do not access data directly but instead through an abstract data model
provided by the DBMS.
- Physical independence: applications immune to changes in storage
structures
- Logical independence: applications immune to changes in data organization
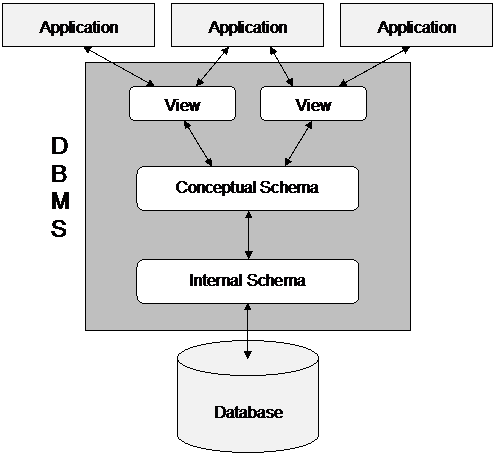
Three Level Schema Architecture
Formalized by ANSI/SPARC (American National Standards Institute,
Standards Planning And Requirements Committee) in 1975
- External schema (view):
what the application programs and users see
- may differ for various users of the same database
- Conceptual schema:
description of the logical structure of all data in the database
- Internal schema:
description of physical structure (selection of files, devices, storage algorithms, etc.)
Types of Database Users
- End user:
- accesses the database indirectly through forms or other query-generating
applications
- generates ad-hoc queries
- Application developer:
- designs and implements application programs that access the database
- Database administrator (DBA):
- manages common database schemas
- assists with application view integration
- monitors and tunes DBMS performance
- defines internal storage structures
- loads and reformats database
- is responsible for security and reliability
Brief History of Database Management
- IBM's Information Management System (IMS) supports hierarchical data model (1968)
- only allows 1:N parent-child relationships (i.e. a tree)
- hierarchy can be exploited for efficiency
- queries navigate up and down trees, one record at a time
- data access language embedded in business processing language (COBOL, PL/1)
- difficult to express some queries and to maintain code
- Charles Bachman (GE) develops Integrated Data Store (IDS) and the network data model (mid 60s)
- standardized by Conference On DAta SYstems Languages (CODASYL) (1969)
- data organized as collections of superimposed sets of records
- N:M relationships can be represented by allowing records to appear in multiple sets
- pointers between records represent relationships
- set types encoded as lists
- queries navigate between records, still one record at a time
- Edgar Codd (IBM) proposes relational data model (1970)
- firm mathematical foundation
- declarative queries
- Charles Bachman wins ACM Turing award for network data model (1973)
- "The Programmer as Navigator"
- Transaction processing for concurrency control and recovery (Jim
Gray and others, mid 70s)
- Peter Chen proposes entity-relationship (E-R) data model (1976)
- IBM's System R and UC Berkeley's Ingres
systems demonstrate feasibility of relational DBMS (late 70s)
- Development of commercial relational technology (early 80s)
- Oracle, IBM DB2, Informix, Sybase
- On-Line Transaction Processing (OLTP)
- Edgar Codd wins ACM Turing award for relational data model (1981)
- SQL standardization through ANSI (1986) and ISO (1987)
- Object-oriented DBMSs
- persistent objects
- object id's, methods, inheritence
- navigational interface reminicent of hierarchical model
- Continued expansion of SQL and system capabilities (SQL-1992, SQL:1999, SQL:2003, SQL:2008)
- Continued commercial and academic implementations
- Object-Relational DBMSs (early 1990s)
- New application areas:
- On-Line Analytic Processing (OLAP)
- data warehousing
- embedded systems
- multimedia
- text, semi-structured data, the Internet, XML
- data streams
- Jim Gray wins ACM Turing award for formalizing transaction processing (1998)
- e-commerce systems
- social media